Enzymes Have How Many Active Sites . Web the enzyme’s active site binds to the substrate. Web enzymes are usually proteins having primary, secondary, and tertiary structures. Web enzyme active site and substrate specificity. Web the enzyme’s active site binds to the substrate. Web the active site of an enzyme is the region that binds substrate molecules. The active site is usually a small region (10% to 20%) within the. The chemical reactants to which an enzyme binds are the enzyme’s. Since enzymes are proteins, this site is composed of a unique combination. Since enzymes are proteins, this site is composed of a unique combination. This is crucial for the enzyme’s catalytic activity.
from www.slideserve.com
Web enzymes are usually proteins having primary, secondary, and tertiary structures. This is crucial for the enzyme’s catalytic activity. Since enzymes are proteins, this site is composed of a unique combination. Web the active site of an enzyme is the region that binds substrate molecules. Web the enzyme’s active site binds to the substrate. Web enzyme active site and substrate specificity. The active site is usually a small region (10% to 20%) within the. Since enzymes are proteins, this site is composed of a unique combination. Web the enzyme’s active site binds to the substrate. The chemical reactants to which an enzyme binds are the enzyme’s.
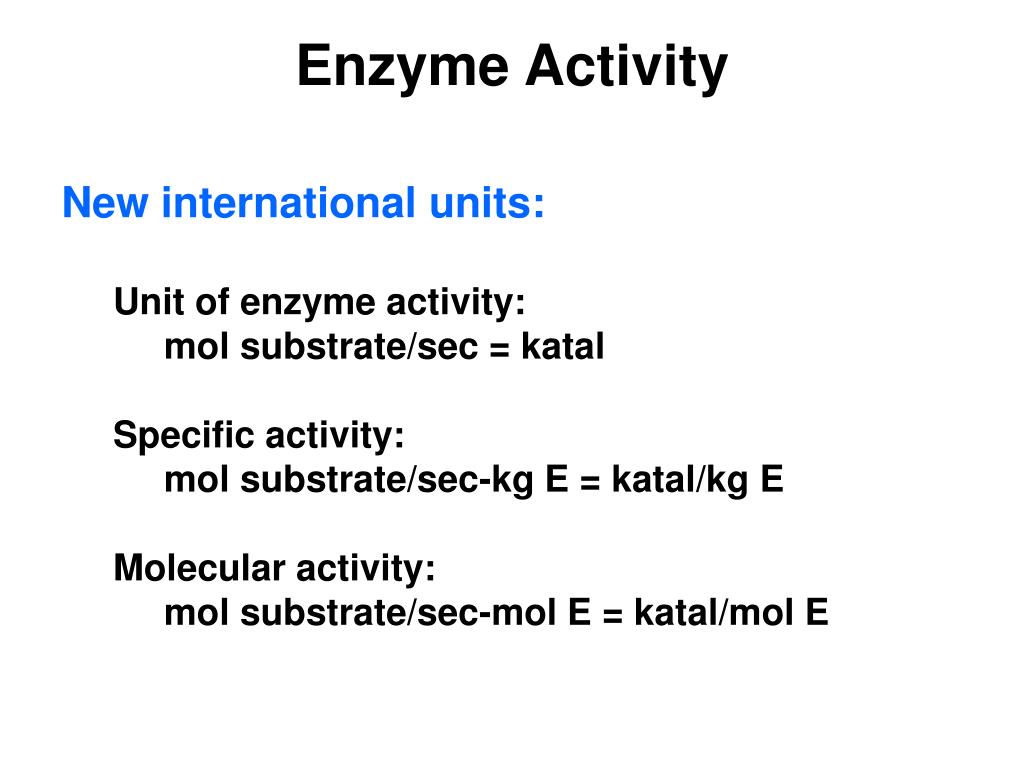
PPT Calculations of Enzyme Activity PowerPoint Presentation, free
Enzymes Have How Many Active Sites The active site is usually a small region (10% to 20%) within the. Since enzymes are proteins, this site is composed of a unique combination. Since enzymes are proteins, this site is composed of a unique combination. Web the enzyme’s active site binds to the substrate. Web enzyme active site and substrate specificity. The active site is usually a small region (10% to 20%) within the. The chemical reactants to which an enzyme binds are the enzyme’s. Web the enzyme’s active site binds to the substrate. This is crucial for the enzyme’s catalytic activity. Web the active site of an enzyme is the region that binds substrate molecules. Web enzymes are usually proteins having primary, secondary, and tertiary structures.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Common features for enzymes and catalysts PowerPoint Enzymes Have How Many Active Sites This is crucial for the enzyme’s catalytic activity. Web the enzyme’s active site binds to the substrate. Since enzymes are proteins, this site is composed of a unique combination. Since enzymes are proteins, this site is composed of a unique combination. The active site is usually a small region (10% to 20%) within the. The chemical reactants to which an. Enzymes Have How Many Active Sites.
From chemistnotes.com
what is active site of enzyme? Chemistry Notes Enzymes Have How Many Active Sites Since enzymes are proteins, this site is composed of a unique combination. Since enzymes are proteins, this site is composed of a unique combination. Web the enzyme’s active site binds to the substrate. Web enzyme active site and substrate specificity. Web enzymes are usually proteins having primary, secondary, and tertiary structures. Web the enzyme’s active site binds to the substrate.. Enzymes Have How Many Active Sites.
From hayasbioblog.blogspot.com
AP Biology Blog Enzymes Enzymes Have How Many Active Sites This is crucial for the enzyme’s catalytic activity. Web enzyme active site and substrate specificity. Web the enzyme’s active site binds to the substrate. Web enzymes are usually proteins having primary, secondary, and tertiary structures. Web the enzyme’s active site binds to the substrate. Since enzymes are proteins, this site is composed of a unique combination. Since enzymes are proteins,. Enzymes Have How Many Active Sites.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Enzymes PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID89282 Enzymes Have How Many Active Sites The chemical reactants to which an enzyme binds are the enzyme’s. Web the enzyme’s active site binds to the substrate. Since enzymes are proteins, this site is composed of a unique combination. Web enzyme active site and substrate specificity. This is crucial for the enzyme’s catalytic activity. Web enzymes are usually proteins having primary, secondary, and tertiary structures. Web the. Enzymes Have How Many Active Sites.
From www.lecturio.com
Definition and Function of Enzymes Online Medical Library Enzymes Have How Many Active Sites Web enzyme active site and substrate specificity. The chemical reactants to which an enzyme binds are the enzyme’s. Since enzymes are proteins, this site is composed of a unique combination. The active site is usually a small region (10% to 20%) within the. Web the active site of an enzyme is the region that binds substrate molecules. Since enzymes are. Enzymes Have How Many Active Sites.
From www.genome.gov
Enzyme Enzymes Have How Many Active Sites Since enzymes are proteins, this site is composed of a unique combination. The chemical reactants to which an enzyme binds are the enzyme’s. Web enzyme active site and substrate specificity. The active site is usually a small region (10% to 20%) within the. This is crucial for the enzyme’s catalytic activity. Web the enzyme’s active site binds to the substrate.. Enzymes Have How Many Active Sites.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Six classes of enzymes PowerPoint Presentation, free download Enzymes Have How Many Active Sites Web enzymes are usually proteins having primary, secondary, and tertiary structures. Since enzymes are proteins, this site is composed of a unique combination. Web the enzyme’s active site binds to the substrate. This is crucial for the enzyme’s catalytic activity. Since enzymes are proteins, this site is composed of a unique combination. The chemical reactants to which an enzyme binds. Enzymes Have How Many Active Sites.
From stock.adobe.com
Active site of enzyme catalyst. Substrate reactants enter active site Enzymes Have How Many Active Sites Web enzyme active site and substrate specificity. Web the enzyme’s active site binds to the substrate. The active site is usually a small region (10% to 20%) within the. Since enzymes are proteins, this site is composed of a unique combination. Web the enzyme’s active site binds to the substrate. The chemical reactants to which an enzyme binds are the. Enzymes Have How Many Active Sites.
From www.lecturio.com
Basics of Enzymes Concise Medical Knowledge Enzymes Have How Many Active Sites Web enzyme active site and substrate specificity. Web the enzyme’s active site binds to the substrate. This is crucial for the enzyme’s catalytic activity. Web the active site of an enzyme is the region that binds substrate molecules. Since enzymes are proteins, this site is composed of a unique combination. Since enzymes are proteins, this site is composed of a. Enzymes Have How Many Active Sites.
From science.halleyhosting.com
Chapter 8 Enzymes Enzymes Have How Many Active Sites Since enzymes are proteins, this site is composed of a unique combination. Web enzyme active site and substrate specificity. Web the enzyme’s active site binds to the substrate. Web enzymes are usually proteins having primary, secondary, and tertiary structures. Web the active site of an enzyme is the region that binds substrate molecules. Since enzymes are proteins, this site is. Enzymes Have How Many Active Sites.
From www.coursehero.com
Energy, Matter, and Enzymes Microbiology Course Hero Enzymes Have How Many Active Sites Web the active site of an enzyme is the region that binds substrate molecules. The active site is usually a small region (10% to 20%) within the. Since enzymes are proteins, this site is composed of a unique combination. Web enzyme active site and substrate specificity. Web the enzyme’s active site binds to the substrate. Web enzymes are usually proteins. Enzymes Have How Many Active Sites.
From cpoclass.com
How enzymes work Talking Pools Podcast News Enzymes Have How Many Active Sites Since enzymes are proteins, this site is composed of a unique combination. Web enzymes are usually proteins having primary, secondary, and tertiary structures. Web enzyme active site and substrate specificity. This is crucial for the enzyme’s catalytic activity. Web the active site of an enzyme is the region that binds substrate molecules. The active site is usually a small region. Enzymes Have How Many Active Sites.
From depositphotos.com
Enzyme substrates and active sites, chemical and biological processes Enzymes Have How Many Active Sites Since enzymes are proteins, this site is composed of a unique combination. Web the active site of an enzyme is the region that binds substrate molecules. Web enzyme active site and substrate specificity. Since enzymes are proteins, this site is composed of a unique combination. Web the enzyme’s active site binds to the substrate. The active site is usually a. Enzymes Have How Many Active Sites.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Enzyme Inhibition and Regulation PowerPoint Presentation, free Enzymes Have How Many Active Sites Web the active site of an enzyme is the region that binds substrate molecules. The active site is usually a small region (10% to 20%) within the. The chemical reactants to which an enzyme binds are the enzyme’s. Web enzyme active site and substrate specificity. This is crucial for the enzyme’s catalytic activity. Since enzymes are proteins, this site is. Enzymes Have How Many Active Sites.
From www.thoughtco.com
Structure and Function of an Enzyme Enzymes Have How Many Active Sites Web the enzyme’s active site binds to the substrate. Web the enzyme’s active site binds to the substrate. Web enzymes are usually proteins having primary, secondary, and tertiary structures. Web enzyme active site and substrate specificity. This is crucial for the enzyme’s catalytic activity. The chemical reactants to which an enzyme binds are the enzyme’s. Web the active site of. Enzymes Have How Many Active Sites.
From www.labxchange.org
LabXchange Enzymes Have How Many Active Sites Web the enzyme’s active site binds to the substrate. Web the active site of an enzyme is the region that binds substrate molecules. This is crucial for the enzyme’s catalytic activity. Since enzymes are proteins, this site is composed of a unique combination. Web the enzyme’s active site binds to the substrate. Web enzymes are usually proteins having primary, secondary,. Enzymes Have How Many Active Sites.
From drawittoknowit.com
Physiology Enzyme Active Site & Regulation ditki medical Enzymes Have How Many Active Sites Since enzymes are proteins, this site is composed of a unique combination. The active site is usually a small region (10% to 20%) within the. Web enzyme active site and substrate specificity. This is crucial for the enzyme’s catalytic activity. Web the enzyme’s active site binds to the substrate. Since enzymes are proteins, this site is composed of a unique. Enzymes Have How Many Active Sites.
From www.youtube.com
How to Calculate Specific Activity of an Enzyme YouTube Enzymes Have How Many Active Sites Web enzymes are usually proteins having primary, secondary, and tertiary structures. Since enzymes are proteins, this site is composed of a unique combination. Web the enzyme’s active site binds to the substrate. Web the active site of an enzyme is the region that binds substrate molecules. Since enzymes are proteins, this site is composed of a unique combination. Web enzyme. Enzymes Have How Many Active Sites.